Lesson 13 - How Night Vision Technology Works
Oct 19th 2023
Introduction
Night vision technology has revolutionized how we see and operate in the dark. From military missions to search and rescue efforts, night vision devices (NVDs) have become essential tools. Armasight, a leading thermal and night vision optics company, has played a crucial role in advancing this technology. In this blog, we'll delve into the fascinating world of night vision and explore how it works.
Types of Night Vision Devices
Night vision devices come in various forms, each with unique capabilities:
- Image Intensifier (I²) Devices: These devices amplify existing light, making it possible to see in near-darkness. They collect and intensify ambient light, rendering it visible to the human eye.
- Thermal Imaging Cameras: Unlike I² devices, thermal imaging cameras don't rely on ambient light. They detect heat emitted by objects and create thermal images based on temperature differences. This technology can be used in complete darkness and challenging weather conditions.
- Fused or Integrated Night Vision Systems (INVSs): These systems combine multiple technologies, such as image intensification and thermal imaging, to provide comprehensive night vision capabilities. This fusion results in a clearer and more detailed image.
- Near Infrared (NIR) Active Illuminator Technology: NIR illuminators emit near-infrared light that is invisible to the naked eye but can be detected by NVDs. They are often used in conjunction with image intensifiers to improve visibility in complete darkness.
Functions of NVDs
NVDs serve various functions depending on their application:
- Detection: NVDs help detect objects in low-light environments, revealing what would otherwise remain hidden.
- Recognition: They allow users to recognize and distinguish objects in the dark.
- Identification: In some cases, NVDs provide the ability to identify specific features of an object, even in the absence of visible light.
- Target Acquisition and Engagement: In military and security contexts, weapon-mounted NVDs enhance the ability to acquire and engage targets under low-light conditions.
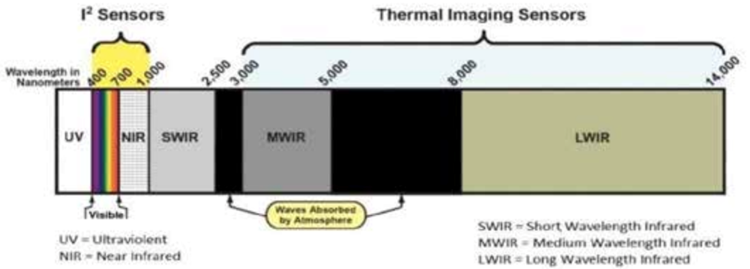
Understanding the Visible Light Spectrum
To grasp how night vision works, it's essential to understand the visible light spectrum. This spectrum represents the narrow band of electromagnetic radiation our eyes can perceive, encompassing colors from violet to red. Each color corresponds to a specific wavelength within this spectrum, ranging from approximately 400 nanometers (violet) to 700 nanometers (red).
The magic of color in the visible spectrum occurs when objects reflect light within this range. For instance, something appears green because it reflects green light while absorbing other colors. This phenomenon creates the vibrant and diverse world we see around us.

Conclusion
Night vision technology has made it possible to explore and operate in the dark with unprecedented clarity. Armasight and similar companies continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in the realm of night vision. Understanding the principles of night vision, including the visible light spectrum, allows us to appreciate the incredible capabilities of these devices.
